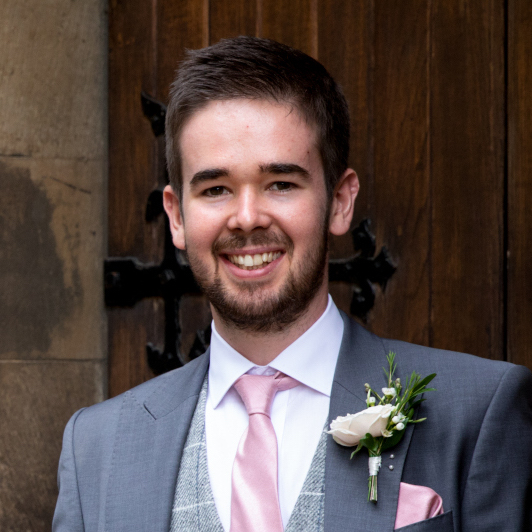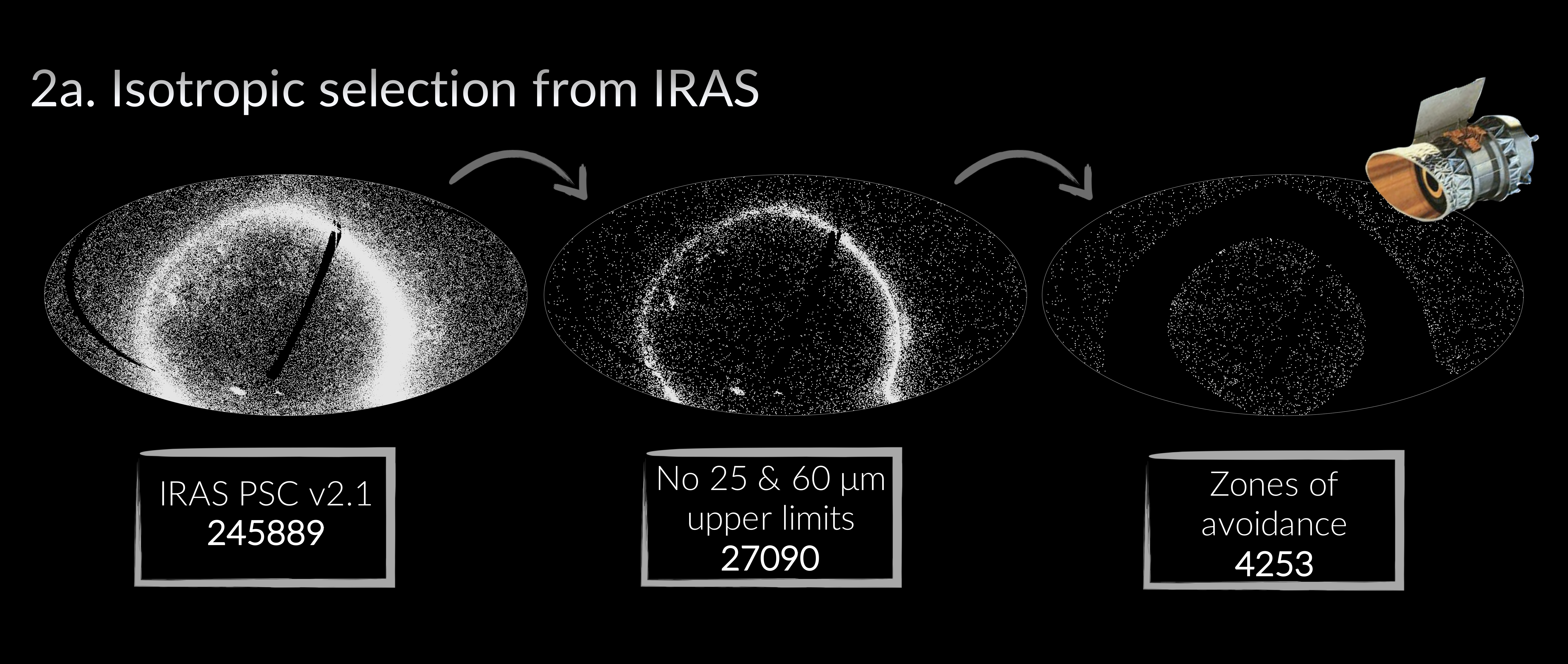
To select AGN isotropically of their intrinsic flux, we used the warm IRAS selection from de Grijp+87 (see also Keel+94) using only detections at 25 & 60 micron in the IRAS PSC v2.1. In the unified model, IR continuum emission arises from dust reprocessing of accretion disc photons in the obscurer, such that the selection should be largely isotropic of Seyfert type.
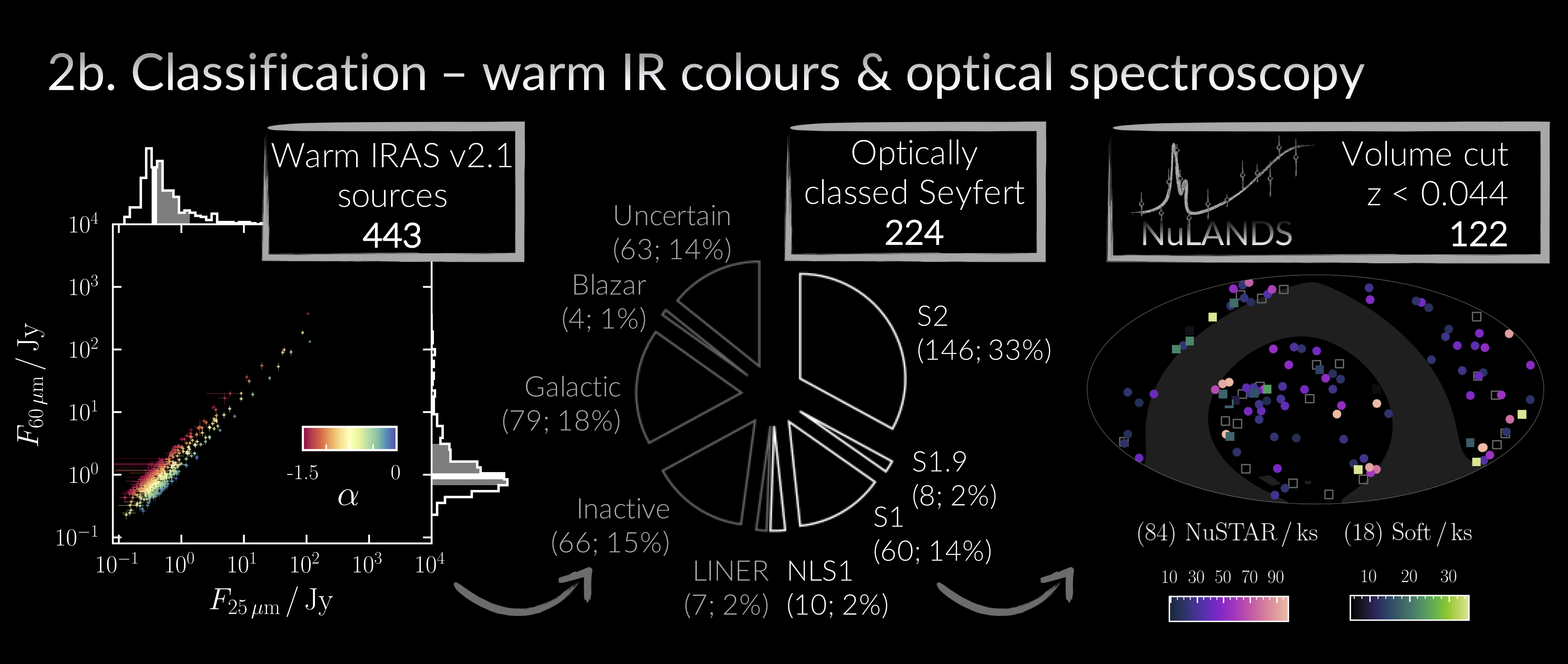
Left: To weed contaminants, we classified warm IRAS sources with the spectral index (alpha) defined in de Grijp+85 to identify flatter (i.e. hotter) IR spectra than cooler inactive galaxies. Middle: Optical spectroscopic classifications were acquired and non-active/ambiguous sources were removed. Right: A volume cut defines the NuSTAR Local AGN NH Distribution Survey - a legacy survey of warm IRAS Seyferts with NuSTAR, Swift, XMM, Chandra & Suzaku.
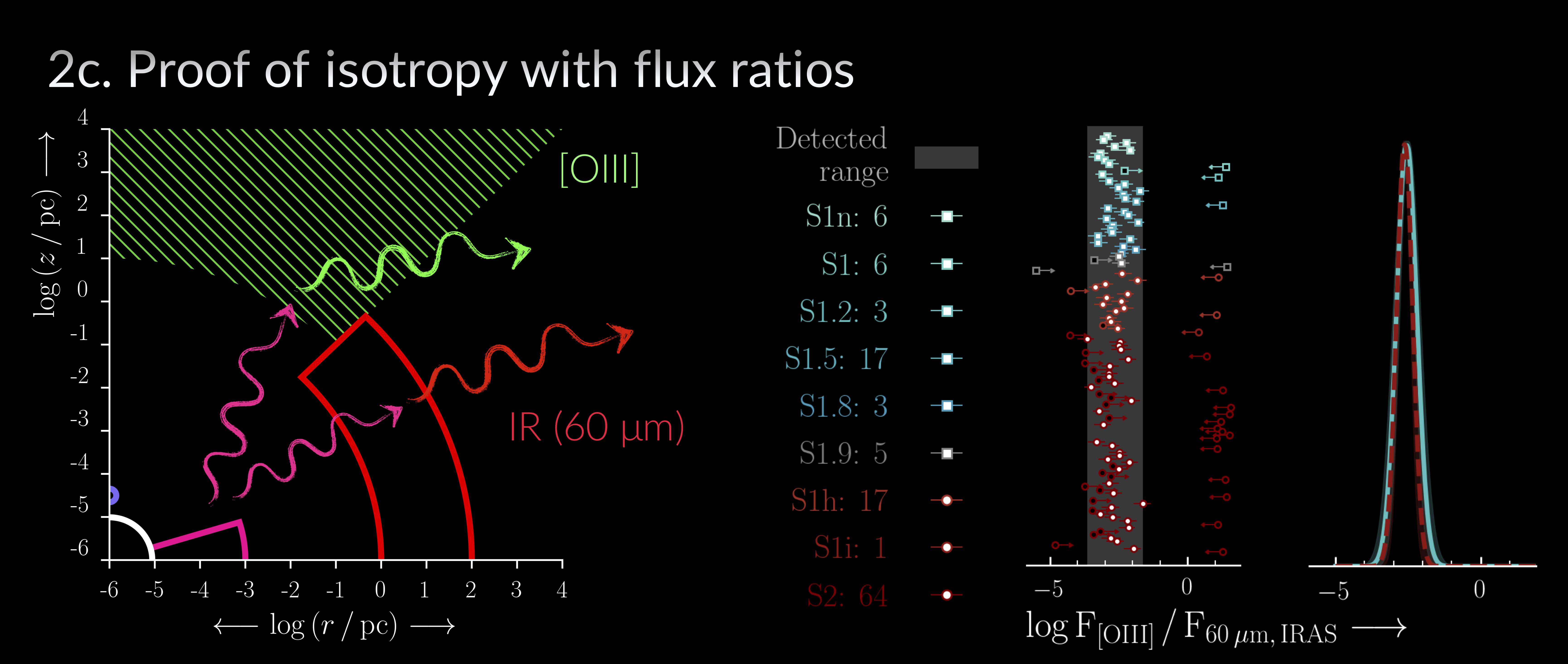
Left: Approximate AGN schematic highlighting the emission processes & size scales associated with the NuLANDS selection & classification techniques. Middle & right: The distribution of [OIII] to 60 micron flux ratios is fit with a Gaussian model using UltraNest separately for type 1 (S1n, S1, S1.2, S1.5, S1.8) and type 2 (S1h, S1i, S2) AGN. The istropic nature of the sample is confirmed from the nearly identical best-fit distributions for type 1 and 2 AGN.